|
ADC with ADS7828 Page posted: 2015-05-16 15:23
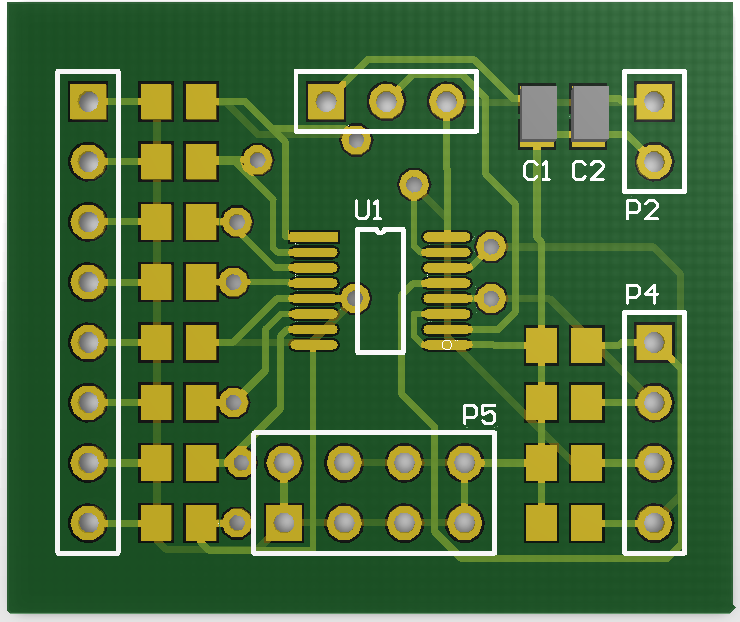 The ADS7828 is a single-supply, low-power, 12-bit data
acquisition device that features a serial I2C interface and an 8-channel multiplexer. The Analog-to-Digital (A/D) converter features a
sample-and-hold amplifier and internal, asynchronous clock. The combination of an I2C serial, 2-wire interface and micropower consumption makes
the ADS7828 ideal for applications requiring the A/D converter to be close to the input source in remote locations and for applications requiring
isolation. The ADS7828 is available in a TSSOP-16 package.
For optimum performance, care should be taken with the physical layout of the ADS7828 circuitry. The basic SAR architecture is sensitive to
glitches or sudden changes on the power supply, reference, ground connections, and digital inputs that occur just prior to latching the output of
the analog comparator. Therefore, during any single conversion for an “n-bit” SAR converter, there are n “windows” in which large
external transient voltages can easily affect the conversion result. Such glitches might originate from switching power supplies, nearby digital
logic, and high-power devices.With this in mind, The ADS7828 is a single-supply, low-power, 12-bit data
acquisition device that features a serial I2C interface and an 8-channel multiplexer. The Analog-to-Digital (A/D) converter features a
sample-and-hold amplifier and internal, asynchronous clock. The combination of an I2C serial, 2-wire interface and micropower consumption makes
the ADS7828 ideal for applications requiring the A/D converter to be close to the input source in remote locations and for applications requiring
isolation. The ADS7828 is available in a TSSOP-16 package.
For optimum performance, care should be taken with the physical layout of the ADS7828 circuitry. The basic SAR architecture is sensitive to
glitches or sudden changes on the power supply, reference, ground connections, and digital inputs that occur just prior to latching the output of
the analog comparator. Therefore, during any single conversion for an “n-bit” SAR converter, there are n “windows” in which large
external transient voltages can easily affect the conversion result. Such glitches might originate from switching power supplies, nearby digital
logic, and high-power devices.With this in mind,
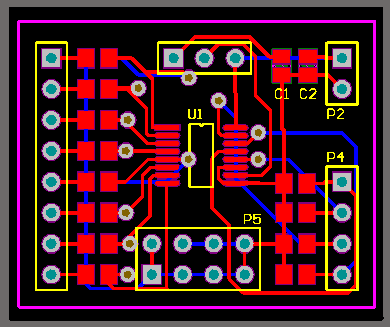 power to the ADS7828 should be clean and well-bypassed.
A 0.1μF ceramic bypass capacitor should be
placed as close to the device as possible. A 1μF to 10μF capacitor may also be needed if the impedance of the connection between +VDD
and the power supply is high. The ADS7828 architecture offers no inherent rejection of noise or voltage variation in regards to using an external
reference input. This is of particular concern when the reference input is tied to the power supply. Any noise and ripple from the supply will
appear directly in the digital results. While high-frequency noise can be filtered out, voltage varia-tion due to line frequency (50Hz or 60Hz)
can be difficult to remove. The GND pin should be connected to a clean ground point. In many cases, this will be the “analog” ground. Avoid
connections that are too near the grounding point of a microcontroller or digital signal processor. The ideal layout will include an analog ground
plane dedicated to the converter and associated analog circuitry. power to the ADS7828 should be clean and well-bypassed.
A 0.1μF ceramic bypass capacitor should be
placed as close to the device as possible. A 1μF to 10μF capacitor may also be needed if the impedance of the connection between +VDD
and the power supply is high. The ADS7828 architecture offers no inherent rejection of noise or voltage variation in regards to using an external
reference input. This is of particular concern when the reference input is tied to the power supply. Any noise and ripple from the supply will
appear directly in the digital results. While high-frequency noise can be filtered out, voltage varia-tion due to line frequency (50Hz or 60Hz)
can be difficult to remove. The GND pin should be connected to a clean ground point. In many cases, this will be the “analog” ground. Avoid
connections that are too near the grounding point of a microcontroller or digital signal processor. The ideal layout will include an analog ground
plane dedicated to the converter and associated analog circuitry.
|